Exploring Google’s Breakthrough in Audioplethysmography for Heart Rate Monitoring in ANC Earbuds
In today’s fast-paced world, we are increasingly concerned about our health, especially heart health. While smartwatches and fitness trackers offer convenient heart rate monitoring, not everyone wears them regularly. Some prefer the simplicity of traditional watches or no wearable devices at all, whether during workouts or casual walks. Google recognized this gap in the wearable technology landscape and has made a groundbreaking stride by incorporating heart rate monitoring into a pair of earbuds. This innovation utilizes a new acoustic sensing system and the field of Audioplethysmography (APG). In this article, we delve into the details of this revolutionary technology and how it can potentially benefit us.
Understanding Audioplethysmography (APG)
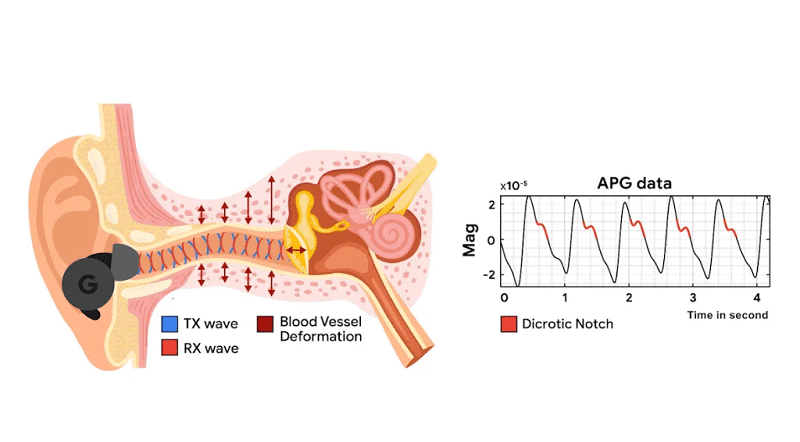
Audioplethysmography, or APG, is a method for measuring blood volume changes in the peripheral circulation using sound waves. It’s a technique that leverages the power of sound to monitor vital signs, particularly heart rate. Google’s innovative approach involves embedding an APG system into their active noise-canceling (ANC) earbuds.
How Do Google’s ANC Earbuds Work?
The ANC earbuds are equipped with a feedback microphone placed inside the ear cup to detect environmental noise and capture the user’s surroundings. This microphone acts similarly to how the human ear perceives sounds. The ANC circuit processes this feedback, creating anti-noise, and then sends the result to the earbud’s speaker, effectively canceling out the external noise. To enhance noise cancellation, Google’s ANC headphones also utilize a feedforward microphone outside the ear cup, working in tandem with the feedback microphone. These microphones do more than just cancel noise; they can detect and record various bio-signals within the ear canal.
Power of Bio-Signal Detection
Google’s technology goes beyond just heart rate monitoring. It can measure heart rate variability (HRV) as well. Remarkably, it does this even in cases of poor earbud seals, and it remains unaffected by variations in skin tones. Ear canal size and less-than-optimal seal conditions do not compromise the accuracy of these readings.
However, the system is sensitive to body motion. To address this, Google has implemented a multi-tone approach that calibrates and selects the best frequency to measure heart rate, ensuring high-quality pulse waveform, even in the presence of movement.
Accurate Results and Comparative Studies
Google conducted extensive studies involving 153 participants to validate the accuracy of their APG technology. The results were impressive, showing consistently accurate heart rate measurements with a median error of just 3.21 percent across all activity scenarios. Furthermore, the technology achieved a median error of only 2.70 percent in inter-beat interval measurements. These findings were compared to data collected from multiple FDA-approved devices, including Masimo MightySat Rx and Nonin 9560 Onyx II Fingertip Pulse Oximeter for heart rate, and Zephyr bio harness 3 and Polar HIO chest strap for ECG and HRV data. Google’s APG system proved to be on par with or even superior to these traditional monitoring methods.
A Cost-Effective and Efficient Approach
What sets Google’s approach apart is its emphasis on software upgrades rather than adding traditional photoplethysmograph (PPG) and electrocardiograms (ECG) sensors or microcontrollers to headphones or earbuds. Traditional sensors add cost, complexity, and weight to these devices, making them impractical for daily use. Google’s APG technology offers a simpler and more cost-effective solution, enhancing the utility of ANC headphones without significant battery life impact.
Future Implications
Google’s research holds promise for the future of wearable technology and health monitoring. The ability to monitor heart rate with a simple software upgrade in ANC headphones could potentially become a standard feature, ensuring that users can keep a constant check on their cardiovascular health. This innovation might also pave the way for blood pressure monitoring using pulse wave analysis.
In conclusion, Google’s foray into Audioplethysmography for heart rate monitoring in ANC earbuds is a significant leap in the wearables industry. It simplifies health tracking and makes it more accessible to a wider audience. With this innovation, we can imagine a future where tiny earbuds play a crucial role in maintaining our heart health consistently.
FAQs
Is Google’s APG technology available in the market now?
Google’s APG technology is currently in the research phase, and there’s no official release date for consumer products.
How accurate is the heart rate monitoring with Google’s ANC earbuds?
Google’s studies have shown consistently accurate heart rate readings, with a median error of just 3.21 percent.
Do these earbuds work with all ear sizes and shapes?
Yes, Google’s technology is designed to work effectively with different ear canal sizes and sub-optimal seal conditions.
Can I use these earbuds while working out or during physical activities?
Yes, Google’s APG technology is suitable for use during various activities, including workouts.
Will this technology drain the battery life of ANC earbuds?
According to Google, the impact on battery life is negligible, making it a practical solution for daily use.